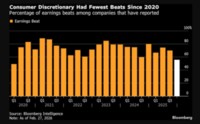
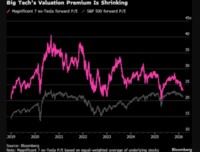
Remarks by Chairman Ben S. BernankeAt the Fifteenth Congressional District of Texas’ Fifth Regional Issues Conference, Washington, D.C., Washington, D.C.,June 13, 2006 Increasing Economic Opportunity: Challenges and Strategies I am pleased to be here to discuss some strategies for helping families, particularly lower-income families, improve their economic and financial well-being. Families today face a financial marketplace that is increasingly complex, with numerous products and service providers from which to choose. Today I will touch on several approaches for helping people of modest means take advantage of these financial opportunities while managing the risks and avoiding possible pitfalls. Today’s Financial Marketplace Technological advances have dramatically transformed the provision of financial products and services in recent years. To cite just one example, the expanded use of computerized credit-scoring models, by reducing the costs of making loans and by increasing the range of assets that lenders can sell on the secondary market, has made possible the extension of credit to a larger group of borrowers. Indeed, we have seen an increasingly wide array of products being offered to consumers across a range of incomes, leading to what has been called the democratization of credit. Likewise, technological innovation has enhanced financial services, such as banking services, and increased the variety of financial products available to savers.The range of providers in consumer financial markets has also increased, with the number of nonbank entities offering credit and other financial services having risen particularly quickly. For example, a recent study of alternative providers of financial services found the number of nonbank check-cashing establishments doubled in the United States between 1996 and 2001.1 Payday lending outlets, a source of credit that was almost non-existent a decade ago, now number more than 10,000. And data from the Survey of Consumers Finances, a triennial survey sponsored by the Federal Reserve Board, indicate that the share of households with a loan from a finance company increased from 13 percent in 1992 to 25 percent in 2004. Financial Challenges of Lower-Income FamiliesDespite the increased complexity of financial products and the wider availability of credit in many forms, U.S. households overall have been managing their personal finances well. On average, debt burdens appear to be at manageable levels, and delinquency rates on consumer loans and home mortgages have been low. Measured relative to disposable income, household net worth is at a fairly high level, although still below the peak reached earlier this decade. Families with low to moderate incomes, however, face special financial challenges. These families generally have less of a cushion to absorb unanticipated expenses or to deal with adverse circumstances, such as the loss of employment or a serious health problem. Results from the Survey of Consumer Finances show that the median net worth for households in the lowest income quintile--those whose income placed them in the bottom fifth of the population--was only $7,500 in 2004, well below the median for all survey respondents of $93,000.2 The Survey data also indicate that households in the lowest quintile were significantly less likely than the average respondent to maintain a checking or savings account; almost 25 percent of those families were "unbanked," compared to less than 10 percent of families in the other income quintiles. The reasons given for not having an account varied: Some respondents said they would not write enough checks to make having an account worthwhile, but others were dissuaded by minimum balance requirements or said that they did not have enough money to justify opening an account. In some cases, a lack of knowledge about the services that banks offer or even a distrust of banks is likely a factor. The Survey also found that lower-income households are less able than others to manage their debts. A greater fraction of these households had debt-to-income ratios of 40 percent or more or had a payment past due at least sixty days. The data also reveal that only 40 percent of families in the lowest quintile own a home, compared with a homeownership rate of 69 percent among all families surveyed. Finally, the data on retirement account ownership show an even larger gap, with only 10 percent of lowest-quintile families holding a retirement account, whereas 50 percent of all families responding to the survey reported participation in some type of retirement savings plan. How can these disparities be addressed? Some general approaches to helping families of modest means build assets and improve their economic well-being include community economic development, financial education, and programs that encourage saving and investment. In the remainder of my remarks, I will discuss each of these approaches briefly and offer some insights into their effectiveness based on research and experience.Community Economic Development In my time with the Federal Reserve, I have had a number of opportunities to meet with community economic development leaders--representatives of groups working to assist lower-income families become homeowners, start small businesses, better manage their finances, and save for the future. In fact, my first trip as a Federal Reserve Board member was to Brownsville, Texas, where I saw how a grassroots nonprofit organization is helping to build communities and to provide residents with the chance to build wealth through homeownership. The Community Development Corporation (CDC) of Brownsville works with multiple funding partners--governments at all levels, financial institutions, foundations, and corporations--to construct housing and to design innovative loan products that enable low-income families to qualify for mortgage credit. For example, because of the mix of funding sources, mortgage loans can be offered with features such as down‑payment assistance or a below-market interest rate. The CDC of Brownsville also offers a program that allows prospective homeowners to acquire "sweat equity" in a property by working on construction teams to help build their own new home and those of other participating families. As in the case of many community development organizations, the Brownsville CDC has also made financial education a critical element of its efforts to help lower-income residents improve their financial status. For example, participation in financial counseling or in an education program is typically required for a borrower to obtain a loan through the CDC or through one of its lending partners. However, the broader aim of these programs is to improve borrowers’ prospects for longer-term success in maintaining their credit and handling their overall finances. Since 1994, through this combination of leveraged financing arrangements and borrower education, the CDC of Brownsville has helped make homeownership possible for more than 2,500 low-income families. I cite the Brownsville example because of the opportunity that I had to learn about their work (and I recently had a similar opportunity to see some impressive community development efforts in the Anacostia neighborhood of the District of Columbia). But this localized approach to community development and wealth-building is playing out in neighborhoods throughout the country, in most cases through strategies tailored to the distinct needs of the particular community.Financial Education and Financial LiteracyFinancial education has not only been integral to community development but has also begun to play a larger role in the broader consumer market. Clearly, to choose wisely from the wide variety of financial products and providers available, consumers must have at least basic financial knowledge. People who understand the financial aspects of purchasing a home or starting a business, or who appreciate the importance of saving for children’s education or retirement, will almost certainly be economically better off than those without that vital information. Financial literacy can be acquired through many channels: in school, on the job, through community programs and counseling, or through self-education and experience.Studies generally find that people receiving financial education or counseling have better financial outcomes. For example, research that analyzed data on nearly 40,000 mortgage loans targeted to lower-income borrowers found that families that received individual financial counseling were less likely later to become delinquent on their mortgage payments.3 Similarly, another study found that borrowers who sought and received assistance from a credit counseling agency improved their credit management, in particular, by reducing the number of credit accounts on which they carried positive balances, cutting overall debt, and reducing delinquency rates.4 More broadly, the research shows that financial knowledge is correlated with good financial outcomes; for example, individuals familiar with basic financial concepts and products have been found to be more likely to balance their checkbook every month, budget for savings, and hold investment accounts.5 Studies that establish an association between financial knowledge and good financial outcomes are encouraging, but they do not necessarily prove that financial training and counseling are the causes of the better outcomes. It could be, for example, that counseling is associated with better financial outcomes because the consumers who choose to seek counseling are the ones who are already better informed or more motivated to make good financial decisions. In medicine and other fields, researchers gain a better understanding of what causes what by doing controlled studies, in which some subjects are randomly assigned a particular treatment while others do not receive it. To translate this idea to the analysis of the effects of financial counseling, the Federal Reserve Board’s Division of Consumer and Community Affairs is collaborating with the Department of Defense to conduct a three-year study of the effects of financial education. This study will evaluate the impact of various educational programs on the financial decisions of soldiers and their families. It includes a treatment group of those receiving financial education, with the programs each family receives and when they receive it being determined randomly, and a control group of similar soldiers and their families who have not received this formal financial education. Because assignments of individuals to programs will be random, any observed changes in behavior can be more reliably attributed to the type and amount of counseling received. Among other things, the results of this study should help us better understand whether financial education leads to changes in behavior for participants in general or only for those at critical teaching moments, such as the period before making a major financial decision such as choosing a mortgage.I would like to say just a few words about the Federal Reserve’s broader role in promoting consumers’ understanding of financial products and services. Beyond conducting surveys of consumers and doing research, we work in a number of ways to support consumers in their financial decisionmaking. For example, through our consumer protection rule-writing authority, the Federal Reserve sets requirements that specify the information that must be disclosed to consumers about the terms and fees associated with credit and deposit accounts. These disclosures provide consumers with the essential information they need to assess the costs and benefits of financial services and compare products among different providers. We are currently reviewing many of our disclosures and plan to use focus groups and other methods to try to make these disclosures as clear and as user-friendly as possible. The Federal Reserve System also works to promote financial education and financial literacy through various outreach and educational activities. We provide a great deal of substantive financial information, including interactive tools for economic education, on our education website www.federalreserveeducation.org. The website links to a wide variety of financial education resources at the local, regional, and national levels.Additionally, the Federal Reserved Board collaborates with educational and community development organizations to support their efforts. Our national partners include the Jump$tart Coalition for Personal Financial Literacy, the Conference of Mayors’ DollarWi$e Campaign, Operation HOPE, the American Savings Education Council, and America Saves, among others. At the regional level, the twelve Federal Reserve Banks work with organizations to support financial education and financial literacy. For example, the Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland has worked with community financial educators to form regional networks that combine resources and share best practices. The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago sponsors "MoneySmart Week," partnering with banks, businesses, government agencies, schools, community organizations, and libraries to host activities designed to help consumers learn how to manage money. The Federal Reserve Banks of San Francisco and Minneapolis have worked with leaders in the Native American community to develop financial education materials. My recent testimony to Congress on financial literacy provided information on many other projects and programs. 6 The Federal Reserve will continue to make financial education a priority.Strategies to Encourage SavingEven if people know that they would be better off if they saved more or budgeted more wisely, we all know from personal experience that translating good intentions into action can be difficult. (Think about how hard it is to keep New Year’s resolutions.) The field of behavioral economics, which studies economic and financial decisions from a psychological perspective, has cast new light on consumer behavior and led to recommendations about how to improve people’s financial management. For example, studies of individual choices in 401(k) savings plans strongly suggest that workers do not pay adequate attention to their saving and investment decisions. Notably, despite the tax advantages of 401(k) contributions and, in some cases, a generous employer match, one-quarter of workers eligible for 401(k) plans do not participate. Studies have found, however, that if firms change the presentation of the plan from an "opt-in" choice to an "opt-out" choice, in which workers are automatically enrolled unless they actively choose to remain out of the plan, participation rates increase substantially.7 The impact of changing from "opt-in" to "opt-out" is particularly evident for younger and lower-income workers, who may have less financial expertise.In addition, participants in savings plans evidently do not understand the various investment options that are offered. A survey by the investment management firm, The Vanguard Group, found that many plan participants cannot assess the risk inherent in different types of financial assets; for example, many did not appreciate that a diversified equity mutual fund is generally less risky than keeping most of one’s wealth in the form of the employer’s stock.8 Indeed, employees appear to invest heavily in their company’s stock despite the fact that their income is already tied to the fortunes of their employer. More than one-quarter of 401(k) balances are held in company stock, and this high share arises not only from an employer match but from voluntary purchases as well.9These insights into consumer behavior have prompted some changes in the design of retirement plans and in education programs focused on saving for retirement. More employers now feature automatic enrollment in their 401(k) plans in an effort to boost participation. Also, some have set the default investment option to a diversified portfolio that is rebalanced automatically as the worker ages or have set contribution rates to rise automatically over time in line with salary increases.However, although these changes in program design may boost saving and improve investment choices, they are not a substitute for continued financial education. Employers, including the Federal Reserve Board, offer financial education at the workplace to help their workers gain a better understanding of retirement savings options. Helping people appreciate the importance of saving and giving them the tools they need to translate that knowledge into action remain major challenges.ConclusionLet me close by observing that many factors influence consumer financial behavior. Financial education is clearly central to helping consumers make better decisions for themselves and their families, but policymakers, regulators, nonprofit organizations, and financial service providers must all help ensure that consumers have the tools and the information they need to make better decisions. Success can only come through collaborative efforts. I see much interest today in increased collaboration toward these objectives, both in Washington and around the country.Thank you for the opportunity to speak with you today. I encourage you to continue working together to help provide increased economic opportunity in your communities, and I wish you the best of luck in your efforts. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------Footnotes1. Kenneth Temkin and Noah Sawyer (2004), "Analysis of Alternative Financial Service Providers (781 KB PDF)," report prepared for the Fannie Mae Foundation by the Urban Institute Metropolitan Housing and Communities Policy Center. 2. Brian K. Bucks, Arthur B. Kennickell, and Kevin B. Moore (2006), "Recent Changes in U.S. Family Finances: Evidence from the 2001 and 2004 Survey of Consumer Finances (448 KB PDF)," Federal Reserve Bulletin. 3. Abdighani Hirad and Peter M. Zorn (2001), "A Little Knowledge Is a Good Thing: Empirical Evidence of the Effectiveness of Pre-Purchase Homeownership Counseling (466 KB PDF)," paper presented at "Seeds of Growth - Sustainable CommunityDevelopment: What Works, What Doesn’t and Why?" 4. Gregory Elliehausen, E. Christopher Lundquist, and Michael E. Staten (2003), "The Impact of Credit Counseling on Subsequent Borrower Credit Usage and Payment Behavior (305 KB PDF" (January), paper presented at "Seeds of Growth - Sustainable Community Development: What Works, What Doesn’t and Why?" 5. Jeanne M. Hogarth and Marianne A. Hilgert (2003), "Patterns of Financial Behaviors: Implications for Community Educators and Policymakers (1.7 MB PDF)," paper presented at "Seeds of Growth - Sustainable Community Development: What Works, What Doesn’t and Why?" 6. Chairman Ben S. Bernanke, Financial Literacy, Testimony Before the Committee on Banking, Housing, and Urban Affairs, U.S. Senate, May 23, 2006. 7. Brigitte Madrian and Dennis Shea (2001), "The Power of Suggestion: Inertia in 401(k) Participation and Savings Behavior," Quarterly Journal of Economics, vol. 116 (November), pp. 1149-87. 8. The Vanguard Group (2002), "Expecting Lower Market Returns in the Near Term," Vanguard Participant Monitor. 9. Jeffrey R. Brown, Nellie Liang, and Scott Weisbenner (2006), "401(k) Matching Contributions in Company Stock: Costs and Benefits for Firms and Workers," Journal of Public Economics, vol. 90 (August), pp. 1315-46.
[관련키워드]
[뉴스핌 베스트 기사]
 사진
사진
의대까지 번진 '사탐런'
[서울=뉴스핌] 송주원 기자 = 2027학년도 대학수학능력시험에서 이른바 '사탐런' 현상이 한층 더 뚜렷해질 것이란 전망이 나온다. 자연계열 수험생들 사이에서 과학탐구(과탐) 대신 사회탐구(사탐)를 택하는 흐름이 빠르게 확산하면서 올해 수능에서는 사회탐구 과목을 1개 이상 응시하는 비율이 80%에 육박할 수 있다는 관측도 제기된다.
다만 입시 전문가들은 사탐 선택이 단순히 탐구 성적만의 문제가 아니라 확보한 시간과 심리적 여유를 국어·수학·영어 등 다른 영역 성적 향상으로 연결할 수 있는지까지 따져 신중하게 판단해야 한다고 조언한다.
대학수학능력시험 사회·과학 탐구 응시 인원 비중 추이. [사진=김아랑 미술기자]
7일 교육계에 따르면 지난해 치러진 2026학년도 수능에서는 사·과탐 영역 응시자 53만 1951명 가운데 77.3%(41만 1259명)가 사탐 과목을 1개 이상 선택한 것으로 집계됐다. 이에 따라 올해 11월 실시되는 2027학년도 수능에서는 그 비율이 80%를 웃돌 가능성도 거론된다.
이 같은 변화는 전통적으로 미적분·기하와 과학탐구 선택 비중이 높았던 자연계 상위권 모집단위에서도 확인된다. 진학사가 정시 지원 대학을 공개한 수험생 자료를 분석한 결과 선택과목 제한이 없는 대학 지원자 가운데 사회탐구 응시자 비율은 의대 9.3%, 수의대 40.5%, 약대 23.8%로 나타났다. 자연계 최상위권에서도 사탐 선택이 더 이상 예외적인 사례만은 아니라는 방증이다.
배경에는 주요 대학의 자연계열 수능 지정과목 폐지가 있다. 주요 대학들이 2025학년도부터 자연계 모집단위에서 응시 지정 과목을 없애면서 사탐·과탐 혼합 응시가 빠르게 퍼졌다. 사탐 응시 비율은 2023학년도 53.3%, 2024학년도 52.2% 수준이었지만 자연계 학과에서 사회탐구를 인정하는 대학이 늘면서 2025학년도 62.2%, 2026학년도 77.3%로 급증했다.
N수생 집단에서도 과탐에서 사탐으로의 이동은 뚜렷했다. 2025학년도와 2026학년도 수능에 연속 응시한 수험생을 보면, 과탐 2과목 응시자 중 19.7%는 이듬해 사탐 2과목으로 23.7%는 사탐+과탐으로 바꿨다. 전년도 사탐+과탐 응시자 가운데서도 62.2%가 올해 사탐 2과목으로 전환했다.
성적 상승 폭도 컸다. 탐구 2과목을 모두 과탐에서 사탐으로 바꾼 집단의 탐구 백분위는 평균 21.68점, 국어·수학·탐구 평균 백분위는 11.18점 올랐다. 과탐 2과목에서 사탐+과탐으로 바꾼 집단도 탐구 13.40점, 국수탐 평균 8.83점 상승했다. 사탐+과탐에서 사탐 2과목으로 전환한 집단 역시 탐구 16.26점, 국수탐 평균 10.92점 올랐다. 사탐 선택이 단순한 유행이 아니라 점수 안정성을 노린 전략적 선택으로 자리 잡고 있음을 보여주는 대목이다.
지난해 12월 13일 서울 성북구 고려대학교 인촌기념관에서 열린 2026 대입 정시모집 대비 진학지도 설명회에서 수험생과 학부모들이 강의를 듣고 있다. [사진=뉴스핌DB]
다만 대학별 반영 방식은 제각각이다. 상당수 대학이 자연계 지원자에게 미적분·기하나 과학탐구 응시 가산점을 주고 있어 지정 과목이 폐지됐다고 해서 유불리가 완전히 사라진 것은 아니다.
국민대·동국대·세종대는 자연계열 지원자가 수학 선택과목으로 미적분이나 기하를 택할 경우 3~5%의 가산점을 반영한다. 성균관대 역시 사회과학계열, 의상학과, 경영학과, 글로벌경영학과, 글로벌경제학과 지원자에게 미적분 선택 시 최대 3%의 가산점을 준다.
과탐 응시자에 대한 가산점도 적지 않다. 경희대·고려대·숙명여대 등은 자연계열 지원자가 과탐을 선택하면 가산점을 부여한다. 서울대의 경우 과탐Ⅱ를 1과목 응시하면 3점, 2과목 응시하면 5점을 추가 반영하며, 과탐Ⅰ만 선택했을 때는 가산점이 없다.
인문계열에서 사탐 선택자에게 가산점을 주는 대학도 있다. 서울시립대는 인문계열 지원자가 사탐 2과목을 응시하면 3%의 가산점을 부여하고, 중앙대는 인문대와 사범대 지원자의 사탐 응시에 5%를 더해 반영한다.
이에 따라 입시 전문가들은 사탐런이 대세처럼 보이더라도 무작정 따라가는 것은 위험하다고 지적한다. 김병진 이투스 교육연구소장은 "많은 학생이 사·과탐 선택에 따른 성적 변화에만 초점을 두지만 핵심은 선택으로 인해 생긴 시간적 여유나 심리적 안정감을 다른 영역 학습에 활용하는 데 있다"며 "사탐 선택으로 줄어든 학습 시간을 국어·수학·영어 등 다른 영역의 성적 향상으로 연결할 수 있는지까지 함께 따져봐야 한다"라고 말했다.
김 소장은 이어 "탐구 과목을 바꿨더라도 결국 같은 학습 시간을 들여야 한다면 입시 전체로 봤을 때 유리한 선택이라고 보기 어렵다"며 "단순히 유행을 좇기보다 자신의 학습 적합성과 대학별 반영 방식, 가산점 구조를 함께 고려해 전략적으로 판단해야 한다"라고 조언했다.
우연철 진학사 입시전략연구소장은 "사탐 응시자가 늘고 이들의 성적이 상승하면서 인문계열 모집단위의 경쟁이 치열해지고, 일부 응시자들은 자연계 모집단위로 눈을 돌릴 가능성이 있다"며 "올해 정시에서는 모집단위별 탐구 반영 방식과 지원 가능 집단의 변화를 함께 고려한 보다 정교한 합격선 예측이 필요하다"라고 강조했다.
jane94@newspim.com
2026-03-07 06:00
 사진
사진
"유가 150달러까지 치솟을 것"
이 기사는 인공지능(AI) 번역을 통해 생성한 콘텐츠로 원문은 3월 6일자 파이낸셜타임스(FT) 기사입니다.
[런던=뉴스핌] 장일현 특파원 = 사드 알카비 카타르 에너지장관은 6일(현지 시간) "전쟁이 중단되지 않으면 며칠 내에 걸프 지역 모든 산유국들이 불가항력을 선언할 것"이라고 말했다.
사드 알카비 카타르 에너지장관. [사진=로이터 뉴스핌]
그는 이날 영국 일간 파이낸셜타임스(FT)와 인터뷰에서 세계 최대 액화석유가스(LNG) 생산·수출 기지인 라스라판(Ras Laffan) 산업단지가 이란 공격으로 '불가항력'을 선언할 수밖에 없었다고 밝히면서 "아직 불가항력을 선언하지 않은 국가들도 며칠 내로 그렇게 할 것으로 예상한다"고 말했다.
알카비 장관은 카타르 국영기업인 카타르에너지의 최고경영자(CEO)를 겸직하고 있다.
불가항력은 지진 등 자연재해나 전쟁 등의 이유로 계약 이행이 불가능하다는 것을 선언하는 것이다. 책임이나 보상 등에서 면제받을 수 있다. 석유나 LNG 등의 계약에 필수적으로 포함되는 내용이다.
카타르는 미국, 호주 등과 함께 세계 3대 LNG 생산·수출국으로 꼽힌다. 현재 연 7700만톤 규모인 노스필드(North Field) 가스전의 생산능력을 오는 2027년까지 1억2600만톤으로 늘리는 프로젝트를 진행하고 있다. 이 프로젝트가 완성되면 LNG 생산과 수출이 세계 1위가 될 것이라는 평가를 받고 있다. 이 가스전의 첫 증산 물량은 올해 3분기에 시장에 나올 예정이었다.
알카비 장관은 "지금 벌어지고 있는 전쟁은 세계 경제를 무너뜨릴 수 있고, 며칠 내에 모든 걸프 지역 산유국들이 생산을 중단하게 되면 유가가 배럴 당 150달러까지 치솟을 수 있다"고 했다.
그는 현재 가동이 중단된 라스라판 LNG 시설에 대해 "지금 당장 전쟁이 끝난다해도 정상적인 사이클로 돌아가는 데 최소 몇 주에서 몇 달은 걸릴 것"이라고 했다.
유럽의 경우 카타르 수출에서 차지하는 비중은 크지 않지만 아시아 구매자들이 시장에서 더 높은 가격으로 가스를 사들이게 되면 덩달아 상당한 고통을 겪게 될 것이라고 전망했다.
FT는 "알카비 장관과의 인터뷰 기사가 나간 뒤 브렌트유는 5.5% 올라 배럴당 90.13 달러를 기록했다"며 "이는 이란 전쟁이 터진 이후 최고 수준"이라고 했다.
알카비 장관은 "이번 전쟁이 몇 주만 더 지속된다면 전 세계 국내총생산(GDP)이 타격을 받을 것"이라고 했다.
모든 국가의 에너지 가격이 상승하고 일부 제품은 부족해질 것이며 원자재 공급이 끊기면서 공장들이 생산을 멈추는 악순환이 펼쳐질 것이라고 전망했다.
중동 지역 국가 중 최대 미군 공군기지가 들어서 있는 카타르는 이란과도 전통적으로 우호적인 관계를 유지해 왔지만, 이번 전쟁의 포화를 벗어나지는 못했다.
라스라판 단지는 지난 2일 이란의 공격 드론의 공격을 받았고, 카타르 정부는 즉각 LNG 생산을 전면 중단했다. 이 단지는 전 세계 LNG 공급의 20%를 담당하는 대규모 시설이다.
알카비 장관은 "군으로부터 해상 시설에 대한 즉각적인 공격 위협이 있다는 통보를 받았고, 즉각 가동을 중단하고 24시간 안에 9000여명의 인력을 철수시켰다"고 했다.
그러면서 "전쟁이 완전히 끝나기 전까지 카타르의 생산은 재개되지 않을 것"이라고 말했다.
ihjang67@newspim.com
2026-03-07 00:20